Health informatics, it also called healthcare informatics. It is information engineering applied to the field of healthcare, essentially the management and use of patient healthcare information. It is a multidisciplinary field that uses health information technology (HIT) to improve health care via any combination of higher quality, higher efficiency and new opportunities.
The NLM defines health informatics health informatics as "the disciplinary study of the design, development, adoption and application of IT-based innovations in health care services delivery, management and planning. It also deals with resources, devices and methods required to optimize the acquisition.

Graves and Corcoran Health Care Informatics
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1046/.1365-2753.2002.00345.x
Schwinian, 1986
Nursing information involves identification of information needs, resolution of the needs and attainment of nursing goals/objectives.
- Patricia Schwirian proposed a model intended to stimulate and guide systematic research in nursing informatics in 1986.
- Model/framework that enables identification of significant information needs, that can foster research (some what similar to Maslow's hieraarchy of needs)
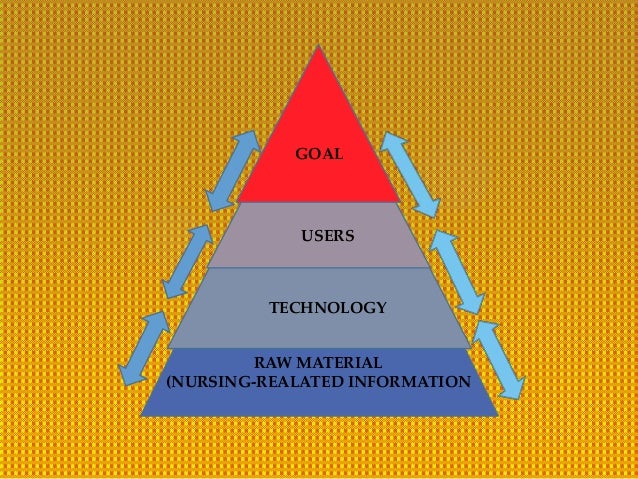
Schwirian Model (1986)
https://www.slideshare.net/minettedin/theories-models-frameworks
Turley's Model 1996
Nursing informatics is the intersection between the discipline-specific science and the area of informatics.
Core components of informatics
- Cognitive science
- Information science
- Computer Science
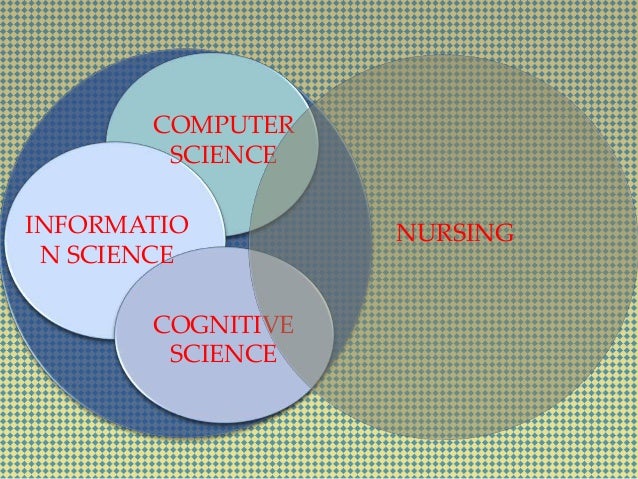
Turley's Models (1996)
https://www.slideshare.net/minettedin/theories-models-frameworks
Dreyfus Model
According to research during the seventies, the dreyfus brothers conducted a thorough research on the topic of how individual obtains and master a skill. they observed people with high quality expertise indifferent spheres and came to the conclusion, that the individual doesn't only acquire more knowledge in his field. they created five stage model which aim to describe the person from obtaining skill to mastering it.
Dreyful's Model
https://www.360pmo.com/the-five-dreyfus-model-stages/
Straggers, Gassert, and Curran, 2001
Valid and comprehensive nursing informatics (NI) competencies currently are lacking. Meanwhile, nursing leaders are emphasizing the need to include NI in nursing curricula, as well as within the roles of practicing nurses in all settings. This article presents the initial work of a team of NI experts toward development of a valid and reliable set of NI competencies. Previous work primarily has focused on computer-related skills, rather than examining a broad definition of informatics competencies. For this current work, NI competencies encompass all skills, not only computer-related skills, as well as knowledge and attitudes needed by nurses. The first two authors created a database of NI competencies from the existing literature. A larger panel of NI experts then affirmed, modified, added, or deleted competencies from this database. Competencies were placed into four distinct skill levels. Definitions of each skill level and an initial master list of competencies are provided.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11596683